OVERVIEW
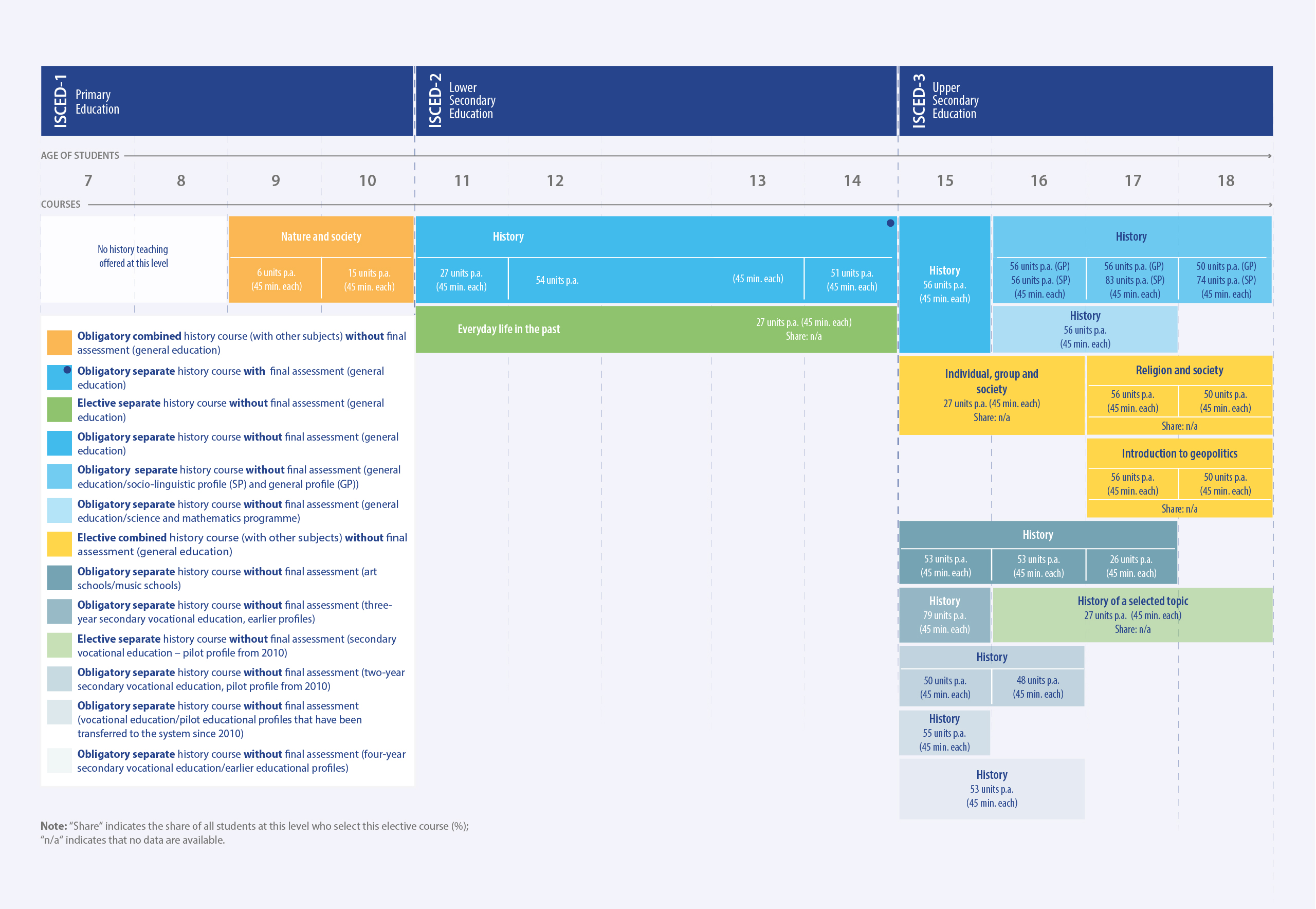
In Serbia, history teaching begins as part of a multidisciplinary course at primary level, becoming a standalone course requiring a final assessment at lower secondary level. At this level, students may take an additional elective course. At upper secondary level, students follow different strands with distinct subject concentrations; these offer both compulsory standalone history courses and elective multidisciplinary courses of various lengths. Vocational education students are required to take a standalone history course at some point at upper secondary level depending on their individual programme.
The history curricula follow a chronological, thematic and competence-based organisation. They are developed by the state with the participation of minority groups, and teachers have a degree of flexibility in the selection of content and teaching methods. History teaching can take place in Serbian or any of eight minority languages. Private schools and schools for national minorities follow the public curricula; the latter include additional content on the cultures and histories of the respective minorities.
Assessment methods include essays, oral presentations/exams, knowledge-based questions, source-based questions, multiple-choice questions, PowerPoint presentations, written reports and research projects. The Ministry of Education issues a catalogue of approved textbooks each school year. And the selection of textbooks to use is made at the school level. Teachers must complete an initial teacher-training programme lasting two academic years, and in-service professional development courses are compulsory.
Download high-resolution schematic
FURTHER INSIGHTS

HISTORY IN SCHOOL
History is taught as part of a compulsory multidisciplinary course, “Nature and society”, over two years at primary level (ages 9-10). Throughout lower secondary education, students are required to take “History” with a final assessment and have the option to also take the course “Everyday life in the past”.
At the upper secondary level, students choose to follow strands with distinct subject concentrations. All students in general education take “History” in the first year at this level (age 15). Students taking the socio-linguistic profile and mathematics profiles thereafter take “History” for three and two more years respectively. General education also offers the elective courses “Individual, group and society” in the first two years at upper secondary level (ages 15-16) as well as “Religion and society” and “Introduction to geopolitics” in the last two years (ages 17-18). Students at art and music schools are required to take “History” for three years (ages 15-17).
For students in vocational education, the inclusion of history depends on the duration of their programme. The two-year and four-year programmes require students to take “History” for two years (ages 15-16) while the three-year programme requires this for the first year only. Under a pilot profile from 2010, vocational education students have the option to study a selected historical topic for three years (ages 16-18).
Teaching takes place in Serbian or any of the eight minority languages (Albanian, Bosnian, Bulgarian, Croatian, Hungarian, Romanian, Ruthenian and Slovak). Schools for national minorities follow the public curricula but include additional content on the cultures and histories of the respective minorities. Private schools follow the same history curricula as public schools.

HISTORY CURRICULUM
The Serbian education system is outlined by the Law on Education (2017), and each subject’s curriculum, including history, is designed to be outcome-oriented. Teachers have a certain degree of flexibility, and can choose content that they consider appropriate and be creative in their teaching process. The only state-imposed limitations on teaching are the aims and objectives of history teaching, some major general themes, some key first-order and second-order concepts, and the learning outcomes defined by curricula. The education authorities reported that minority groups also participate in curriculum development, although representatives of civil society organisations do not.
|
AIMS REPRESENTED “VERY WELL” OR “QUITE WELL” IN THE CURRICULUM |
PERIODS |
GEOGRAPHICAL SCOPE |
APPROACHES |
|
|
|
|
The authorities report that minority groups (cultural, ethnic, linguistic, national, religious or sexual/gender) are included in the history curriculum.
Curricula workstation by GEI (History curricula search by country)

ASSESSMENT AND EXAMS
The assessment methods teachers are required to use are essays, oral presentations/ exams, knowledge-based questions, source-based questions, multiple-choice questions, PowerPoint presentations, written reports and research projects.
End-of-stage examinations are taken for the compulsory lower secondary course “History”, which are set at the national level.
End-of-stage examinations assess the following fields of knowledge: historical content knowledge and historical thinking competences (e.g., critical analysis and evaluation of evidence, formulation and justification of historical arguments, consideration of different perspectives).
End-of-stage examinations are written and consist of open-ended questions, closeended questions, source-based questions and multiple-choice questions.

TEXTBOOKS AND OTHER RESOURCES
Textbooks are written mainly by private entities. The Institute for Education Development evaluates their quality and makes recommendations to the Ministry of Education, which issues a catalogue of approved textbooks each school year. The selection of textbooks to use is made at the school level. The ministry does not license or check any other additional teaching materials or online resources that teachers might use in class. The curriculum is designed to ensure that every teacher has the freedom to create and design additional teaching materials on any topic, regardless of whether or not they are present in textbooks.
Policies on the use of different types of educational resources are as follows:
|
|
|
International TextbookCat (GEI collection of Textbooks and Educational Media)

HISTORY TEACHERS AND THEIR EDUCATION
The initial teaching programme lasts two academic years: one year at bachelor’s level and one at master’s level. This can be taken at university faculties offering history (Belgrade, Novi Sad, Niš, Kosovska Mitrovica). Candidates are required to gain credits in pedagogical, didactic, psychological and methodological subjects as well as through practical teaching experience in schools.
At both primary and secondary levels, teachers are trained exclusively or primarily as history teachers.
In-service professional development courses are compulsory. They are administered by the Ministry of Education, university faculties, non-governmental organisations, history teachers’ associations and the Institute for the Improvement of Education. Accredited training programmes cover topics such as Jewish culture and history, past and present antisemitism, multiperspectivity and the modern history of south-eastern Europe, and the Yugoslav Wars of the 1990s.
Association for Social History – EuroClio (presentation by EuroClio)
Association for Social History – EuroClio (official website)
Education for the 21st Century (presentation by EuroClio)
The information in the sections above is an excerpt of the thematic and general data presented in the following OHTE publications:
2022: Pandemics and natural disasters as reflected in history teaching
2023: OHTE General Report on the State of History Teaching in Europe