OVERVIEW
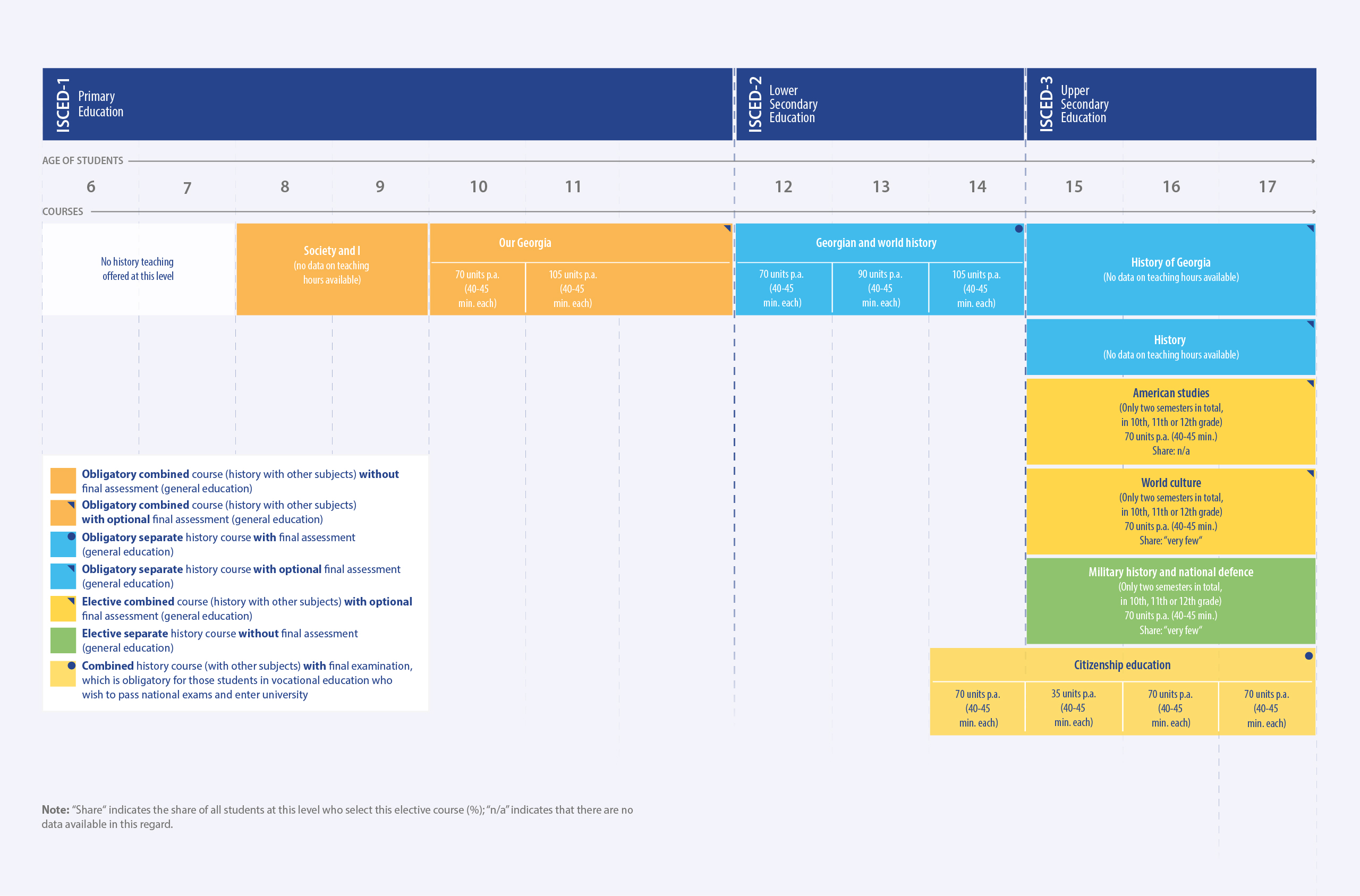
In Georgia, history is taught as part of a compulsory multidisciplinary subject beginning in the third grade of primary school (age 8). In lower secondary education, it is a standalone course with a final assessment. In upper secondary education, some courses are compulsory without a final assessment, while others are optional and may or may not require a final assessment.
The history curriculum is developed using an objectives-based approach. Courses are chronological, thematic and/or competence based. Both civil society organisations and minority groups participate in this process. Privately operated religious schools offer distinct history curricula while schools for minorities use the same national curricula.
Assessment methods include portfolios, essays, oral presentations/exams, knowledge-based questions and source-based questions. All history textbooks must be approved by the Ministry of Education and Science. History teachers must complete an initial teacher-training programme, with all teachers holding at least a bachelor’s or an equivalent academic degree in the relevant subject area or having completed a military/sports professional education. In-service professional development programmes organised by national education authorities are compulsory while those organised by professional associations and non-governmental organisations are optional.
Download high-resolution schematic
FURTHER INSIGHTS

HISTORY IN SCHOOL
In primary school, history is taught as part of two compulsory multidisciplinary courses, “Society and I” in grades 3 and 4 (ages 8-9) and “Our Georgia” in grades 5 and 6 (ages 10-11); the latter course includes an optional final assessment. At lower secondary level, the course “Georgian and world history” is compulsory and requires a final assessment. At upper secondary level, two courses, “History of Georgia” and “History”, are compulsory but have an optional final assessment. Two other courses, “American studies” and “World culture”, are optional with an optional final assessment. Another optional course, “Military history and national defence”, does not have a final assessment. Vocational education students wishing to proceed to tertiary education are required to take the multidisciplinary course “Citizenship education”, including a final assessment.
There are private schools in Georgia, including privately operated religious schools offering distinct history curricula. There are also schools for Armenian, Azerbaijani and Russian minorities; these follow the curricula of the public school system and teach in Armenian, Azerbaijani (Azeri Turkish) and Russian respectively.

HISTORY CURRICULUM
The third-generation national curriculum is an objective-based document. Each subject standard is based on general objectives and concrete objectives (outcomes and concepts) specific to the subject area at primary, lower secondary and upper secondary stages, mandatory topics and objectives within the topics. Based on the New School Model introduced in 2018, modern approaches aimed at the holistic development of the student are promoted, which encourage teachers to use active pedagogies to strengthen students’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills, while developing their creativity. The basic history standard consists of the following elements:
- objectives of teaching the subject;
- results and content of the standard;
- methodological guidelines; and
- evaluation.
At the basic level, the subject of history refers to the integrated teaching of Georgian and world history.
The education authorities report that both civil society organisations and minority groups participate in curriculum development.
|
AIMS REPRESENTED “VERY WELL” OR “QUITE WELL” IN THE CURRICULUM |
PERIODS |
GEOGRAPHICAL SCOPE |
APPROACHES |
|
|
|
|
The authorities report that minority groups (cultural, ethnic, linguistic, national, religious or sexual/gender) are included in the history curriculum. These do not include Roma and Travellers.
Curricula workstation by GEI (History curricula search by country)

ASSESSMENT AND EXAMS
The assessment methods teachers are required to use are portfolios, essays, oral presentations/exams, knowledge-based questions and source-based questions.
End-of-stage exams are compulsory for the compulsory lower secondary course “Georgian and world history”. They are also compulsory for the course “Citizenship” for students in professional/vocational education wishing to take entrance exams to transition to university education.
End-of-stage exams are optional for the compulsory upper secondary course “History”, the compulsory upper secondary course “History of Georgia”, the optional upper secondary course “American studies” and the optional upper secondary course “World culture”.
No data are available regarding the assessment methods and aims in end-of-stage exams.

TEXTBOOKS AND OTHER RESOURCES
Textbook teaching is the predominant form of teaching in Georgia, and textbooks must be approved by the Ministry of Education and Science. Other resources used in history classes, such as historical sources, films and mass media, are selected by the teachers. Teachers have some flexibility in delivering the curriculum and can choose the most appropriate and relevant issue(s) for their students and the methodologies most appropriate to teach them.
Policies on the use of different types of educational resources are as follows:
|
|
|
|
International TextbookCat (GEI collection of Textbooks and Educational Media)

HISTORY TEACHERS AND THEIR EDUCATION
To undergo the teacher-training educational programme, a person must have at least a bachelor’s or an equivalent academic degree in the relevant subject area or military/sports professional education. They are required to pass the relevant subject exam, in this case history, which is organised under the remit of the National Assessments and Examination Centre (NAEC) and the National Centre for Teacher Professional Development (TPDC). After this exam, the candidate must also pass an interview or exam conducted by the higher education institution providing the training course. The teacher-training educational programme lasts for at least one academic year.
Teachers at both primary and secondary school levels are trained to teach history and one or more other discipline(s).
Compulsory in-service professional development programmes are organised by national education authorities, namely the Ministry of Education and Science and the National Centre for Teacher Professional Development. Various professional associations and non-governmental organisations provide optional programmes on specific subjects, including tolerance in multi-ethnic and multireligious societies, the use of different types of sources, conflict-sensitive education and peacebuilding-oriented education.
Georgian Association of History Educators (presentation by EuroClio)
Georgian Association of History Educators (official website)
The information in the sections above is an excerpt of the thematic and general data presented in the following OHTE publications:
2022: Pandemics and natural disasters as reflected in history teaching
2023: OHTE General Report on the State of History Teaching in Europe